Managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) with a Ketogenic Diet
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine condition that affects millions of women worldwide and results in approximately one in ten affected women in Australia having difficulty conceiving. The condition affects the ovaries, often leading to various combinations of elevated testosterone levels, irregular or infrequent ovulation and irregular periods. On ultrasound, one or both ovaries may appear enlarged and contain cysts.
PCOS is associated with insulin resistance. The presence of insulin resistance in PCOS escalates the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, lipid disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers such as breast and endometrial cancer. Correcting insulin resistance by reducing dietary carbohydrate intake, has been shown to be beneficial for managing PCOS. The dietary therapy approach should aim to achieve specific objectives, including symptom control, enhancing insulin sensitivity, improved metabolic function, and optimal reproductive health.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder characterized by imbalanced levels of male reproductive hormones (usually present in women in small amounts), insulin resistance, and multiple small cysts (fluid-filled sacs) on the ovaries. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals but commonly include irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth (hirsutism) on the face or body, acne, weight gain, and infertility. While the exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, factors such as genetics, insulin resistance, and inflammation are believed to play significant roles in its development.
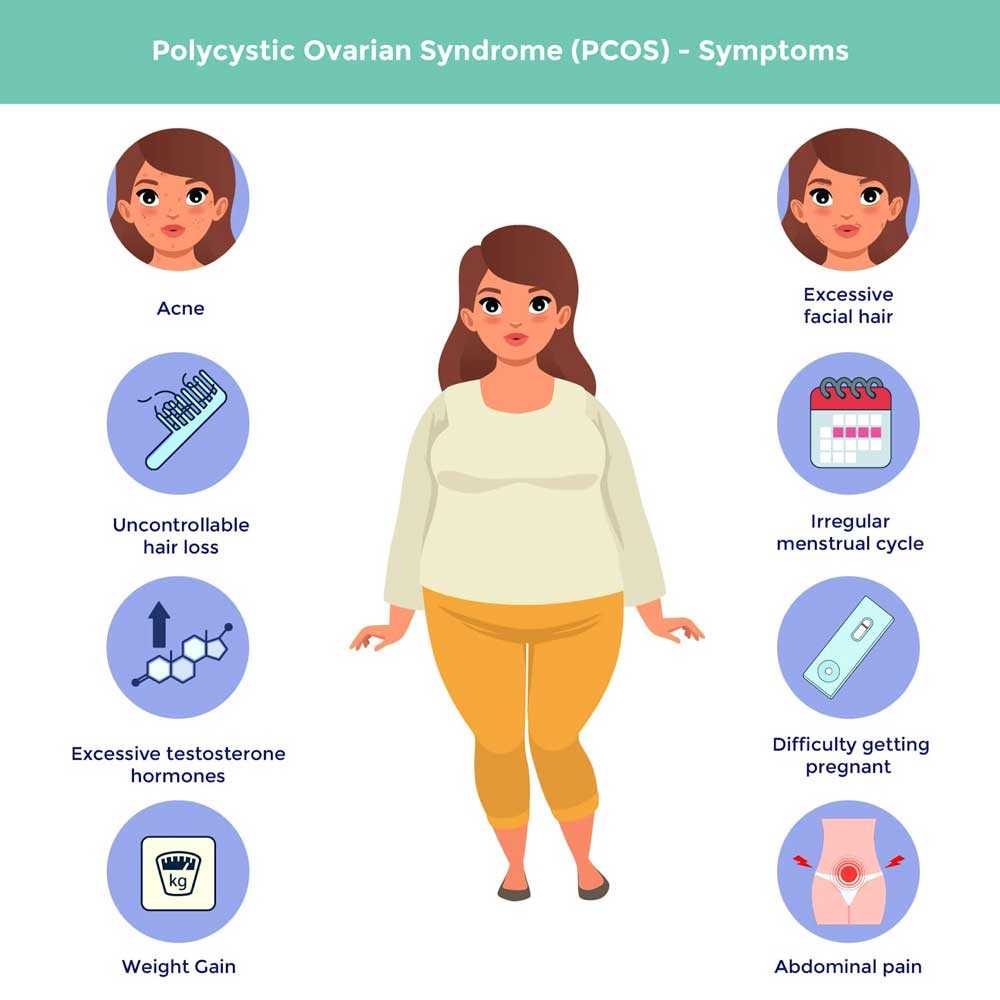
The Role of a Ketogenic Diet in PCOS Management
A ketogenic diet, characterized by high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate intake, has gained attention for its potential therapeutic effects in various health conditions, including PCOS. By reducing carbohydrate consumption, the body enters a state of ketosis, where it primarily burns fat for fuel instead of glucose. This state of ketosis can offer several potential benefits for women with PCOS by correcting insulin resistance and reducing inflammation
A ketogenic diet encourages weight loss and reduces fat mass, which leads to decreased insulin secretion after eating, improving insulin sensitivity, and helping glucose tolerance. Adopting a ketogenic diet has been observed to lower androgen levels and restore the balance ratio of luteinizing hormone (LH) to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), helping to encourage follicular growth and ovulation.

Benefits of a Ketogenic Diet for Women with PCOS
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a notable condition of PCOS, contributing to metabolic dysfunction and weight gain. By reducing carbohydrate intake and consequently lowering blood sugar levels, a ketogenic diet helps mitigate insulin resistance. With improved insulin sensitivity, cells become more receptive to insulin’s actions, leading to better blood sugar control and reduced blood insulin levels. This metabolic shift is crucial for managing PCOS symptoms, as insulin resistance exacerbates hormonal imbalances and contributes to various metabolic disturbances associated with the condition.
Hormonal Balance
PCOS is characterised by imbalanced levels of reproductive hormones, including testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone. Elevated levels of testosterone contribute to symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and irregular menstrual cycles. A study suggests that a ketogenic diet has been shown to influence hormone levels in favour of hormonal balance, as well as reductions in testosterone levels in women6, thereby reducing symptoms such as hirsutism and acne. By restoring hormonal balance, ketosis helps regulate menstrual cycles and improve fertility outcomes for women with PCOS.
Weight Management
Weight gain and obesity are common concerns for women with PCOS, further increasing metabolic dysfunction and hormonal imbalances. A ketogenic diet promotes weight loss and aids in weight management through several mechanisms. Firstly, the high protein content of the diet induces a feeling of satiety, reducing overall calorie intake and promoting adherence to the dietary regimen. Secondly, ketosis enhances fat oxidation and metabolism, leading to increased fat loss compared to traditional low-fat diets. Additionally, the stabilising effect of ketosis on blood sugar levels helps prevent spikes and crashes in energy, reducing cravings and binge eating behaviours commonly associated with PCOS.Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of PCOS and contributes to its associated complications, including insulin resistance, ovarian dysfunction, and cardiovascular risk. Ketogenic diets have been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects, largely through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory signalling pathways and the production of inflammatory mediators. By reducing systemic inflammation, ketosis helps alleviate symptoms and improve overall health outcomes in women with PCOS.
Enhanced Fertility
Infertility is a significant concern for women with PCOS, often attributed to irregular ovulation and hormonal imbalances. By reducing insulin resistance, and restoring hormonal balance and ovulation, the ketogenic diet leads to improved fertility outcomes.

Scientific Evidence Supporting Ketogenic Diet for PCOS
Numerous scientific studies have explored the efficacy of a ketogenic diet in managing PCOS symptoms:
- A new meta-analysis published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society reveals a potential connection between the ketogenic diet and fertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The findings show the keto diet may decrease testosterone levels as well as improve other hormonal imbalances commonly found with PCOS. All the studies reviewed showed significant weight loss.
- A study published in the journal Fertility and Sterility found that a ketogenic diet led to improved insulin resistance, and improvements in triglycerides/HDL-C ratios, and 70% of women with PCOS in the study achieved ongoing pregnancy when combined with IVF.
- A research report published in Frontiers suggests that the Mediterranean Diet Combined With a Low-Carbohydrate Dietary intake helps to restore the menstrual cycle in overweight PCOS patients, improving anthropometric parameters and correcting their disturbed endocrine levels.
Summary
A ketogenic diet holds enormous potential as a therapeutic intervention for women with PCOS, offering many benefits ranging from weight management and improved fertility to hormonal balance and metabolic health. While further research is warranted to clarify the long-term effects and optimal dietary strategies, the existing evidence highlights the transformative impact of low-carbohydrate diets in alleviating the burden of PCOS. By embracing a ketogenic lifestyle, individuals with PCOS can embark on a journey towards improving their quality of life naturally.
References
- Women with PCOS can stress less about fertility. Moss, K., UQ News, The University of Queensland, 2023. https://www.uq.edu.au/news/article/2023/11/women-pcos-can-stress-less-about-fertility
- Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome. National Library of Medicine 2004. [PubMed] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14688154/
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome: Environmental/occupational, lifestyle factors; an overview. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. National Library of Medicine 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6883751/
- Weight management through lifestyle modification for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: rationale and strategies. A statement of the American Diabetes Association, the North American Association for the Study of Obesity, and the American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Klein, S., et al., The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2004. https://shorturl.at/beBJ8.
- Ketogenic Diet as Medical Prescription in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Barrea, L., et al., National Library of Medicine 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9974679/
- Effects of Ketogenic Diet on Reproductive Hormones in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Khalid, K., et al., Journal of the Endocrine Society 2023. https://academic.oup.com/jes/article/7/10/bvad112/7259972#
- The effects of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet on the polycystic ovary syndrome: A pilot study. Mavropoulos, J., et al., National Library of Medicine 2005. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1334192/
- Effects of a ketogenic diet in overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Paoli, A., et al., Journal of Translational Medicine 2020. https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-020-02277-0
- Keto Diet May Improve Fertility in Women with PCOS, Study Finds. Vogel, K., Healthline 2023. https://www.healthline.com/health-news/keto-diet-helps-improve-pcos-symptoms-infertility
- Mediterranean Diet Combined with a Low-Carbohydrate Dietary Pattern in the Treatment of Overweight Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients. Mei, S., et al., Frontiers (vol 9) 2022. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.876620/full
- Nutritional management in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A review study. Faghfoori, Z., et al., Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews (Vol 11), 2017. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1871402117300115?via%3Dihub
