How your body makes energy
From the three available macronutrients - carbohydrates, fats, and proteins - the body preferentially burns carbohydrates, then fats and finally proteins for fuel.
When carbohydrates are available, they are broken down into glucose (a sugar), and as it is released into the blood stream, the levels of insulin (a hormone) are increased to facilitate cellular uptake of glucose. Your body and brain will then use glucose as their primary fuel. Excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscle as glycogen and then released later for energy as needed.
Insulin levels regulate carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism (the processes in which the body converts these to energy), with higher insulin levels shutting down the metabolism of the latter two. In this way, energy is generated from carbohydrates when they are present.
When blood glucose is not available, insulin levels are correspondingly low, and the body turns to burning fat for fuel. This can either be fat that has been eaten or stored as body fat. Fats are broken down into smaller compounds known as fatty acids, which are converted in the liver to ketone bodies (ketones) and subsequentialy burned as fuel by the body.
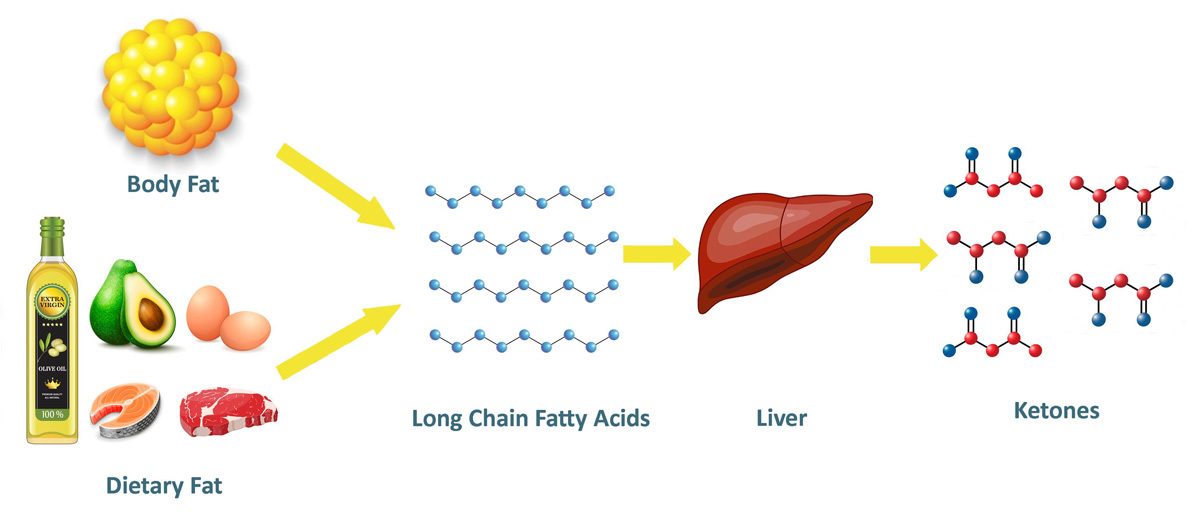
What does it mean to be in Ketosis?
This state is known as nutritional ketosis. It is a physiological state which has been the normal status of human beings for most of our evolutionary history.
Ketones are used as a source of fuel, particularly for the brain, the heart and skeletal muscles.
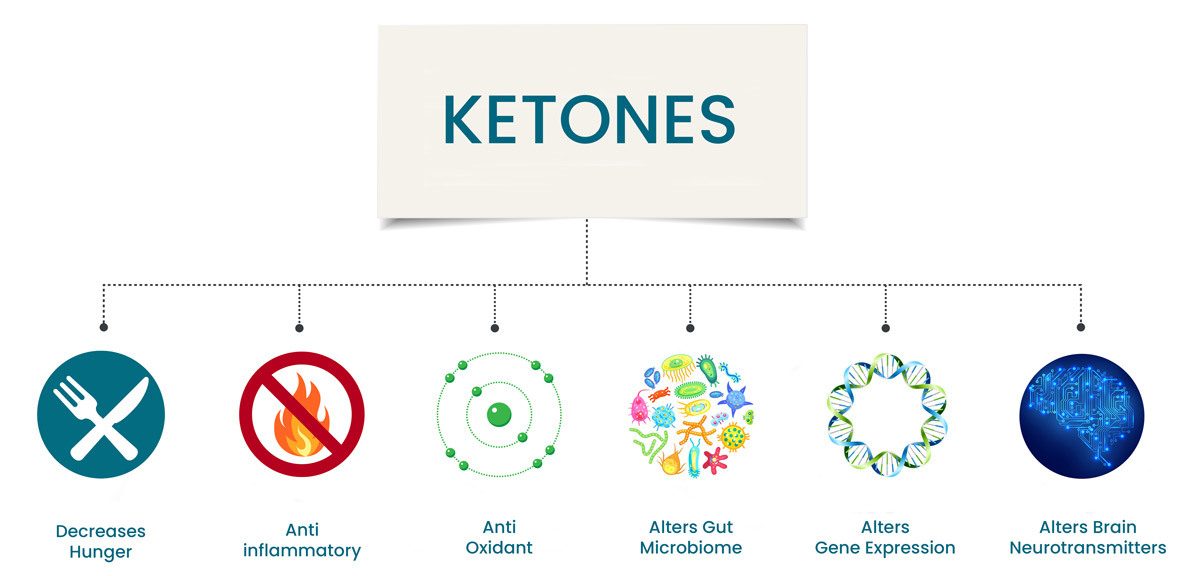
As well as providing fuel for the body, ketones have several potentially beneficial actions, including:
- The sustained reduction of hunger
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Anti-oxidant effects
- Changing the organisms residing in our gut (known as the gut microbiome)
- Changing the way genes are expressed within our DNA (known as epigenetics)
- Altering the production of neurotransmitters (molecules used by the nervous system to transmit messages between neurons).
This may explain why ketogenic diets are emerging as a potential treatment for a broad range of conditions effecting multiple areas of the body including:
- Insulin resistance otherwise known as metabolic syndrome
- High Blood Pressure
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Neurological disorders
- Epilepsy
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Migraine
- Lipoedema
- Chronic Pain
Once established and stable, nutritional ketosis is associated with a feeling of mental clarity and wellbeing.
Nutritional Ketosis vs. Ketoacidosis
Nutritional ketosis and diabetic ketoacidosis are entirely different, and it is an important distinction to understand. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a medical emergency, whereas nutritional ketosis is safe and offers many health benefits.
Unlike nutritional ketosis, Ketoacidosis is a life-threatening condition which can occur:
- When the body produces insufficient insulin, or
- In response to some medications. (This includes drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors which are used for type 2 diabetes, cardiac and renal diseases), or
- With prolonged starvation.
These conditions lead to an elevation in the level of ketones (keto) in the blood together with a decrease in the pH of the blood (acidosis). Ketoacidosis is associated with symptoms of excessive thirst and urination, stomach pain, nausea and vomiting and in its later stages, confusion.
Ketoacidosis mainly occurs in people with type 1 diabetes when they are not getting enough insulin to meet their needs. As a result, blood sugar and ketones rise to dangerous levels. As mentioned above, some medications, such as SGLT2 inhibitors carry a risk of developing Ketoacidosis as well.
Neither a well formulated ketogenic diet nor therapeutic fasting will put you at risk of ketoacidosis unless you a are a type 1 diabetic or you are taking a SGLT2 inhibitor.
Nutritional Ketosis and the Ketogenic diet
A ketogenic diet is one where you reduce the number of carbohydrates you consume and prioritise protein and good fats instead. The exact amount of carbs that will induce ketosis varies from person to person. However, the general rule of thumb is that you will need to reduce your carbohydrate intake to 50 grams per day or even less.
On a ketogenic diet, you will need to reduce or remove carbohydrate-rich and sugar-rich foods from your diet. This includes foods like:
- Grains
- Fruit
- Legumes
- Potatoes
- Processed sugar
- Soft drinks
A qualified keto dietitian will be able to develop a ketogenic nutrition plan to support your current lifestyle and health goals.
How long does it take to enter ketosis?
The short answer is that it the length of time it takes to enter ketosis varies from person to person. Factors like the amount of physical activity you do, your age, metabolism, and carbohydrate, fat and protein intake will influence how long it takes your body to enter ketosis. Typically, once you have reduced your carbohydrate intake to 50g per day, it takes between two to four days to enter ketosis.
Common signs and symptoms of ketosis
If you intentionally follow a ketogenic diet, you may wonder if you have reached ketosis. The most definitive way to confirm ketosis is by checking your blood ketone levels. When you are in ketosis you will have blood ketone levels of 0.5-3 millimoles per litre. You can also measure ketone levels in your urine, using Ketone Testing Strips at home.
When you are following an individually tailored ketogenic nutrition plan, you will more than likely just feel normal. Over time, many people report experiencing increased mental clarity.
Summary
Nutritional ketosis occurs naturally in the body when it uses fat for fuel rather than carbohydrates. This physiological state is kicked off when you reduce the amount of carbohydrates in your diet, and your body seeks out different energy sources. Fat is the body's preferred energy source when carbohydrates aren't available. As a result, your body turns fat into ketones and uses them as fuel for the brain, the heart and skeletal muscles.
Our qualified keto dietitian, doctors and coaches will help you to adapt your diet to prioritise proteins and fats and reduce carbs safely to help you achieve your health and lifestyle goals.
